.jpg)
Organic farming and sustainable Agriculture
Raghvendra Kumar Kushwaha –( Research Scholar PG)
Guru Dayal - (Field Coordinator)*
M.Sc. (Agri.) Soil Science,
Sam Higginbottom University of Agriculture,
Technology and SciencesAllahabad-211007,U.P
Corresponding author Gmail- rkk18200@gmail.com
*Self-Reliant Initiatives Through Joint Action (SRIJAN),
Regional office, Mahavir Nagar,
Manikpur, Chitrakoot, U.P.
Gmail– gurudayal20195@gmail.com
5. Types of organic Farming-
Crops are grown using organic fertilizers in a technique of farming known as organic farming. The application of which lowers the cost per hectare, enhances the soil’s physical, chemical, and biological qualities, as well as its fertility, and also boosts yield per hectare. It is separated into the two major sections listed below.
I. Pure Organic farming - This is a from of farming technique where we only use fertilizer that is entirely made of organic materials. Examples include blood and bone meals.
II. Integrated organic farming- In this method, farming is carried out using both integrated pest management and nutrient management.

6. Importance of Organic farming –
With organic farming, you may produce more food for less money, and the results are of good quality. The following are some significant contributions that organic farming makes to agriculture.
A. Reducing soil erosion
B. Provide high nutrition food
C. Increasing soil fertility
D. Lower input costs
E. Lessen pollution
F. Pest and disease resistance
A. Reducing soil erosion- Using organic fertilizer like manure and vermicompost will help reduce soil erosion. Increases the soil’s ability to store water while reducing soil erosion. For instance, you could plant grass and plants, add mulch, or plant fiber logs.
B. Provide high- nutrition food- Organic farming allows us to produce more pure goods per hectare, which allows us to provide high-quality postic foods.
C. Increasing soil fertility- The fertility of the soil increase quickly and is maintained for a very long time when organic fertilizer is used in the soil. And as result, more is produced per hectare.
D. Lower input costs- Producing more and most at a lower cost is the basic goal of organic farming. Utilising it in agriculture lower the cost per hectare and raises the farmer’s income. And the earth is still in good condition.
E. Lessen pollution- Its usage in the field enhances the soil’s physical, chemical, and biological qualities while lowering the pollution brought on by the use of chemical fertilizer, including water, soil, and air pollution, among other things. Therefore, the environment enhances the health of the soil.
F. Past and disease resistance- In the field, combining Integrated Pest Management with Integrated Nutriment Management encourages plant resistance. It causes the plant’s immunity to rise quickly when used.
7. Advantages of Organic farming
This is a type of agricultural method that increases productivity per hectare while producing products that are absolutely pure and rich in nutrients. The soil’s structure is enhanced by its use. Adopting this will result in the following advantages, which are as follows.
- It is less expensive to use.
- It enhances the soil’s physical, chemical, and biological qualities.
- It prolongs the life of the soil and boosts its fertility.
- It boosts the soil’s ability to store water and its microbial activity.
- It may be used with little expertise.
- Offer nourishing food.
- Reduces soil and water contamination, thus it is environmentally friendly.
- It decreases soil erosion and strengthens plants’ resistance to pests and disease.
- Reduces soil erosion.
- It boosts farmers’ earnings and is practical for use in the field.
- Adopting it doesn’t take a lot of knowledge.
- Does not cause soil damage.
- Possibility to grown a range of crops.
8. Disadvantages of organic farming-
It takes more effort to farm organically, and it is not practiced everywhere. The products made from it are substantially more expensive because it is grown in some locations. To use it in the field, more information is needed. Periodically, the field must be checked. The authentication process is really difficult. For two to three years after adoption, it is obtained in extremely little amounts. The following forms of losses are brought on by using it. More information is needed.
- Information is needed.
- Products cost a lot of money.
- More prone to illness and pests.
- Expensive and inadequate marketing.
- Low Yield, relatively.
- More time-consuming.
- To get a result, more times is needed.
- Market Difficulties.
- Authentication is an extremely difficult process.
- Organic produce typically spoils more quickly.
9. Sustainable Agriculture
Industrial agriculture is responsible for the production of a sizable amount of the food we generate. Industrial agriculture uses a variety of chemicals and pesticides for crop production, which significantly reduces soil fertility or causes contamination of the water, air, and environment. Industrial agriculture has significantly reduced the availability of natural resources. The phrase sustainable agriculture was created to help with this. His intention was to continue farming after the next generation. There was a focus on natural products in huge amounts due to the growing population, for which agrochemical were employed in big quantities. Franklin H. King, an American scientist, described historical farmers in his 10907 book “Farmers Of Forty Centuries.” He provides detailed information on sustainable agriculture and discussed its advantages, noting that this technique will be highly advantageous in the future. We explained. The Australian agronomic Gordon Mc. Clymont is credited with coining the term “sustainable agriculture.” In the later 1980s, the phrase gained popularity.
The quality of natural resources like soil and water affects how much is produced by agriculture. The National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) was the primary focus of sustainable agriculture. Its primary goal was to highlight the components of efficient water usage, nutrition, management, and economic diversification. So that integrated agriculture and the preservation of natural resources can lead to sustainable agriculture are as follows.
- Protecting natural resources for future generations.
- Improve the state of the environment and natural resources.
- To provide for human needs on a daily basis while preserving the environment.
- Make use of the biological cycle and regulation.
- Long-term maintenance of the farm’s financial health.
10. What is Sustainable Agriculture-
The USDA Nation described sustainable agriculture as an integrated set of practices for both plant and animal production in 1977. To put it simply, “ Sustainable agriculture is such a method of agricultural production, in which keeping in mind the environmental resources or meeting the daily needs of people without destroying the natural resources while achieving maximum production or natural resources for the future generations.”
The following three factors, which are categorized as follows, are the key drivers of sustainable agriculture.
1. Environment
2. Society
3. Economy
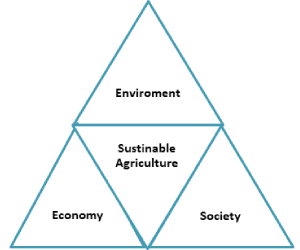
Figure 2- Sustainable agriculture given equal weight to environmental, social, and economic concerns in agriculture.(Source- B. Sonja et. al, 2011)
11. Principal of Sustainable Agricultural-
The major goals of agriculture are to provide for human needs while not depleting natural resources, to produce healthy, long- lasting food, and to lessen soil and water pollution so that future generations can make efficient use of natural resources.
- Long-term maintenance of soil fertility or nutrient levels during the creation of manure.
- Enhancing resource utilization efficiency is essential for the sustainability of agriculture.
- Helping farmers transition to sustainable agriculture by avoiding industrial agriculture and safeguarding the environment.
- Direct actions are needed for the sustainable to conserve, protect, and improve the natural resources.
- Agriculture cannot be sustained if it does not maintain and enhance the rural lifestyle and social welfare.
- Agriculture can only be sustainable if people, communities, and ecosystems are made more resilient.
- A responsible and efficient governance framework is required for sustainable agriculture and nutrition.
- Reducing pollution of the soil, water, and air while protecting the ecosystem.
- To produce more food at a lower cost and boost farmers’ income.
12. Method and technique of Sustainable Agricultural-
Sustainable agriculture’s major objective is to avoid diminishing natural resources so that future generations can make good use of them. More production or meeting human needs is the primary objective of farming. By enhancing the soil’s physical, chemical, and biological qualities as well as its ability to hold more water and the number of earthworms that live there, sustainable agriculture helps keep the soil healthy. The following are the various method that are employed in sustainable agriculture.
1. Cover Crops
2. Agro- forestry
3. Permaculture
4. Hydroponics
5. Urban agriculture
1. Cover crop- Farmers utilise some crop known as “cover crop” to cover the soil. Their use decreases soil erosion, stops weed development in the field, and improves soil fertility. These are the several sorts of crops that are employed in this. Example includes barley, fava, sorghum, and triticale.
2. Agro-frosty- By employing it in the soil, agro-forestry is a technique employed in some forms of sustainable agriculture. Reduces nutrient flow and enhances soil structure. It effectively protects the soil. Additionally, it is significant source of income for farmers, allowing them to easily stop soil erosion. Example- Reetha (Sapindus mukorossii), Banj (Quercus leucotrichophora), and Khaina (Ficus cunia).
3. Permaculture- David Holmgren and Bill Mollison are the authors of the term “Permaculture,” which originally meant “Permaculture agriculture” (Holmgren, D., 2002). It is a system that uses natural principles to guide the growth of human settlements, enabling people to coexist peacefully with the environment. ( Source- Shreya Das et. al., 2020).
4. Hydroponics- Plants are grown hydroponically, a revolutionary agricultural technique that does not require soil. Aquaculture, nutriculture, soilless culture, and tank farming are alternate names for hydroponics. Six different kinds of hydroponic systems exist.
A. Wicking systems
B. Deep water Culture(DWC)
C. Nutrient film Technique (NFT)
D. Ebb and Flow
E. Aeroponics
F. Drip Systems
5. Urban agriculture- Urban agriculture is a sort of agricultural practice that involves growing food for home use and human consumption in and around a city or town. Wherein fruits and veggies are raised utilizing gardening techniques.
13. Benefits of Sustainable agriculture-
The Indian government administers a number of programmers to advance sustainable agriculture. The National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA), one of these programmers, was launched in 2014-2015 as part of the 12th year plan. Its main goal was to follow the road of sustainable agricultural growth, integrated agriculture, and resource conservation. Development of Rainfed Areas, Sub-Mission on Agro- forestry, Soil Health Management, and Climate Change & Sustainable Agriculture were the major four categories under which these components were categorized. Following are some of the many advantages that sustainable agriculture receives from utilizing all these programmers.
- Contributes to environmental safety.
- Prevents and lessens the occurrence of soil and climatic pollution.
- It enhances the soil’s physical, chemical, and biological properties.
- It promotes increased output and nutritional quality preservation.
- Long-term assistance in preserving soil fertility,
- Less risk to the environment.
- Encourages opportunity in rural areas and family farms.
14. Conclusion-
As discussed in the above write-up, the idea of following the organic and sustainable farming is a much better idea than the use of chemicals. Although the outcomes will be a quite late to occur but still the satisfaction will be more than the imagination. The effect of organic farming on human health and nature is observed astonishingly improving. After watching these results there is a change observed in the pattern of treating the agricultural production technology. Also as stated by the institutions working on this goal, the production by this way is a little late but satisfying in the context of human health so the awareness must be spread throughout the sector to save the nature. This way of farming is a labor requiring field, so ultimately it is a big help for employment generation, hence maintaining the employment, wealth and economy for the nation.
15. Reference-
APEDA, (2019-2022). The Ministry Of Commerce & Industry, Government Of India.
Annual Report.
B. Sonja et. al., (2011) Sustainable Agriculture, The nature education knowledge.
Dr. A. Sailaja, (2021) Organic Farming for Sustainable Agriculture, Extension Education
Institute, Hyderabad and National Institute of Agriculture Extension Management
(MANAGE), Hyderabad, India. 40p.
S.S. Rana, (2011) Organic Farming, Research Gate. 4p.
Shreya Das et. al., (2020) Sustainable agriculture: a path towards better future, ResearchGate.
23p.








